Methods of molding:
Metal injection molding(MIM) is the process of injecting metal powder into a mould to form a part with a final shape. MIM combines both plastic injection and metal powder technologies to enable the mass production of precision metal parts using plastic moulding methods.
MIM process technology is fruit of plastic molding technology, polymer chemistry,powder metal technology and etc.MIM overcomes the disadvantages of traditional machining of metal products(low density,material uneven,low mechanical property and hard to mold for thin-wall parts),manufacture fine structural parts with complex shapes, high precision and high performance.
The MIM process is divided into 4 steps:
1. Blending(materials manufacturing):
combines fine metallic powders with an organic binders to form a mixture having good Rheological properties,mixing ratio is very important because the nature of the particles determines the mechanical properties of the metal injection-moulded parts.
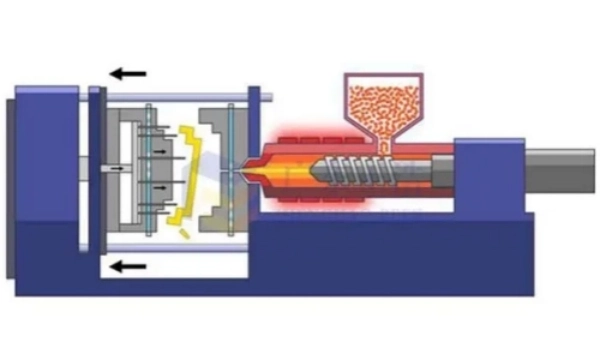
2.Injection(metal injection):
using advanced MIM molding machine to inject compound from resins into tooling cavity in the material to forms a “raw part” of a fixed shape.this process is very similar to plastic injection molding which is available in a variety of sizes.
3.De-binder(degreasing technology):
through chemical solvent dissolving,degreasing is the process of removing the binder from the “raw part”, after which a “brown part” is obtained.
4. Sintering:
In the vacuum furnace of the MIM, the binder and other impurities are removed and the metal powder is densified at temperatures close to the melting point (2700 Fahrenheit scale) to form a complete metal structure, which is then cooled down to obtain the sintered metal part in its finished form,the gaps between the particles disappear due to the fusion of the particles, ultimately achieving the required density and hardness.
Sintering Process:
1.Video Link: Sintering process in the manufacture of metal parts
2.Link: Why are powdered metal parts sintered?