Sintered parts are simple to process, produced with ‘zero waste’, and offer excellent mechanical properties and durability. Regardless of the industry that can take advantage of powder metallurgy, sintered parts have transformed many industries by providing reliable performance and the ability to customize designs, and the applications for low-cost metal powders are seemingly endless!
Pressing and Sintering in Powder Metallurgy
Sintered parts process: A proportioned mixture of metal powders is fed into a manufacturing mold and compacted by a press to produce the “ raw ” part. The “ raw ” parts are then fed into a high temperature furnace for sintering. The metal sintering process provides the final sintered part with complete mechanical properties as a fully formed metal product that can be directly applied to your project without additional machining.
Step 1:Powder Production
Materials can be admixed, pre-alloyed, partially alloyed or a hybrid alloy.
Type of powder used can include stainless steel-based, iron-based, copper-based, metals & non-metallic combinations.Metal raw materials are processed into fine metal powders. These metal powders have a uniform particle size and high purity,and provide a good basis for subsequent processing. Our engineers add the correct proportion of polymers, such as lubricants, graphite, etc., for your application.
Each sintered part has a metal powder mixture determined according to the customer’s needs to ensure that the metal product meets the requirements for high density,high hardness,tolerances, dimensions, impact strength, and mechanical wear resistance, and strives to exceed the customer’s expectations.
* All of our sintered metal parts meet industry and international standards.

Step 2:Compacting
Pressing is one of the key processes of powder metallurgy, which is used to avoid deformations caused in follow-up processes.
The specially formulated metal powder is automatically fed into a precision mold and compacted into the desired shape under 500~600MPa pressure.Under extremely high pressure, the powder is pressed into “parts” of fixed shapes and sizes.
They fulfill all the required dimensions and tolerances and require no additional machining. Our team of skilled engineers is skilled in designing and manufacturing the molds in-house and finally pressing them into “blanks” in a dedicated workshop.
- When it comes to compacting, we offer multiple multi-action presses, ranging from 45 to 1000 tons.

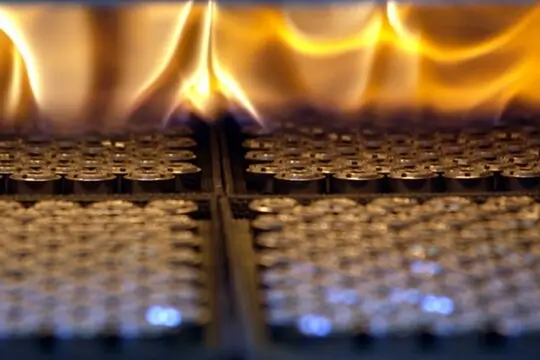
Step 3:Sintering
The pressed parts are quite fragile and need to be deburred before moving them from the press to the furnace. The workpieces, after sintering , have better strength. The sintering furnace is fully automated and can reach temperatures up to 2600°F.
The sintering step transforms the mechanical bond of the compacted powder into a metallurgical bond , providing the strength and performance needed for your powder metal part. The sintered part is ready for use, and if additional processing is required, the sintered part can be immediately subjected to secondary processing or other types of finishing operations.
Sintering process link:
1.Video Link: Sintering process in the manufacture of metal parts
2.Link: Why are powdered metal parts sintered?
Step 4:Secondary Process
Sintered metal parts can often be used in projects without secondary machining. The reduction in machining greatly reduces costs . Sintered metal parts are the preferred choice for most applications.
- To further improve their properties, sintered parts can be subjected to secondary operations. Among these, surface hardening or carburizing processes can be used to increase the hardness of the part’s surface and enhance its resistance to wear and abrasion.
- Osweypm offers plating (in trivalent zinc chromates, nickel, nickel zinc or chrome). We also offer machining,specialized packaging,with de-burring,steam treat and with heat treat.

Learn about a more efficient and precise metal injection molding process that creates complex geometries?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines the design flexibility of plastic injection molding with the strength and durability of metal materials to obtain low-cost, shaped metal parts by molding plastics, and is currently a popular choice in the automotive, power tool, aerospace, and medical industries.
